
THCJD: 6 questions to learn everything about this mysterious cannabinoid
1. What is THCJD?
Tetrahydrocannabinol, often abbreviated as THCJD or THC-JD, is a cannabinoid extracted directly from the hemp plant , like CBD and THC.
However, it is much less abundant than these two cannabinoids. This is why professionals in the legal hemp sector who offer products containing THCJD generally opt for a synthetic version, created in a laboratory from precursors such as CBG, CBD or THC .
As its name suggests, THCJD has a molecular structure very similar to THC, which is, let us remember, the molecule responsible for the psychotropic and addictive effect of cannabis.
The only difference lies in the side chain, which is "alkyl" in THC and "octyl" in THCJD. For chemistry enthusiasts, the octyl chain is the result of an alkyl chain to which three methylene groups (CH2) have been added.
2. Is THCJD psychotropic?
THCJD is ultimately slightly modified THC, whether in its natural state (in the hemp plant) or in a test tube in the laboratory.
Its proximity to THC in terms of molecular structure leaves no room for doubt: THCJD is indeed a psychotropic cannabinoid.
Simply put, like THC, it acts on the state of the central nervous system to alter brain functions, resulting in temporary changes in perception, mood, consciousness, and behavior.
It is therefore a hallucinogenic psychotropic drug , as opposed to stimulant psychotropic drugs (such as amphetamines or caffeine) and depressants (such as alcohol and benzodiazepines).
3. Is THCJD addictive?
THCJD is also an addictive cannabinoid, unlike CBD and similar molecules like CBG, CBN, and CBC. This addiction is explained by four factors.
THCJD and the brain's reward system
Like THC, THCJD binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, particularly the CB 1 receptor, which influences the limbic system, which is involved in emotional responses and memory formation.
By stimulating this system, THCJD stimulates the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and satisfaction. We are therefore in a reward system that will encourage consumption to reproduce pleasant sensations.
THCJD and the phenomenon of tolerance
With regular and prolonged cannabis use, the brain can begin to adapt to the presence of THCJD.
This adaptation will manifest itself through a progressive decrease in the sensitivity of endocannabinoid receptors. The user will therefore have to administer increasingly larger quantities to obtain the same effects. This is what is called "tolerance."
THCJD and addiction
As tolerance develops, users may also develop physical dependence on THC.
In practice, their body will get used to functioning in the presence of the substance, and its absence will trigger the usual withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, insomnia, appetite disorders and anxiety.
THCJD and compulsive behaviors
In addition to physical dependence, psychological dependence can also develop with THCJD.
It manifests itself as an intense and pressing desire to consume cannabis despite knowledge of the side effects on health and the impact on social and professional life.
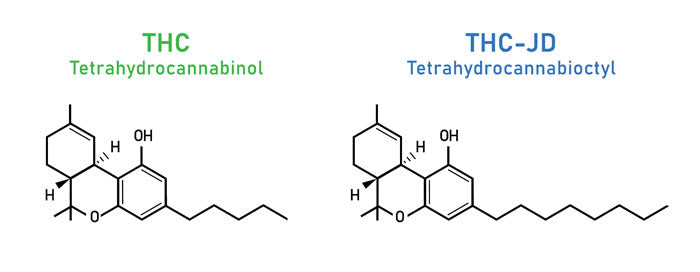
4. What are the differences between THC and THCJD?
As mentioned above, the molecular structure of THCJD features an octyl side chain, which contains three more methylene groups than THC. This structural difference results in three major differences.
THCJD has more affinity with CB1 receptors of the endocannabinoid system
THCJD interacts more strongly with CB1 receptors, located mainly in the brain.
This high interaction could amplify the psychoactive effects of this cannabinoid, including feelings of well-being, relaxation, and pain management. This higher affinity may also extend the duration of the effects, with an experience that is both more intense and longer-lasting.
On the other hand, this property will also increase the risk of tolerance and the speed at which the body becomes dependent. Therefore, it will gradually take higher doses to achieve the same effects, and withdrawal symptoms will be more pronounced when consumption stops.
The importance of this affinity for CB1 receptors reflects both the therapeutic potential of THCJD, but also the risks associated with its use.
THCJD is metabolized more slowly
The rate of cannabinoid metabolism influences the degree of absorption as well as the rate of distribution and elimination in the body.
The fact that THCJD is metabolized more slowly means that the effects appear very gradually after consumption . Their duration will also be longer.
THCJD's slow metabolism may be beneficial for users seeking prolonged relief from symptoms like pain or anxiety, without the highs often associated with THC.
However, it also requires careful attention to dosage and frequency of use to avoid excessive accumulation in the body which could lead to long-term adverse effects.
THCJD is more lipophilic than THC
THCJD dissolves more easily in fats and oils compared to aqueous media. This property affects how it is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted from the body.
When consumed, THCJD more easily crosses cell membranes , which are primarily composed of lipid layers. This characteristic can potentially increase its bioavailability in the central nervous system, where it can exert more pronounced psychoactive effects by interacting with cannabinoid receptors.
On the other hand, since lipophilic compounds tend to accumulate in fatty tissues, THCJD may have a longer half-life in the body compared to THC.
5. What are the benefits sought by THCJD consumers?
Like all cannabinoids, THCJD has several beneficial effects such as:
- A calming and relaxing effect, even sedative, because the substance is more powerful than CBD;
- Anti-inflammatory properties;
- Analgesic properties, which relieve pain, whether acute or chronic;
- An antioxidant action.
Obviously, these virtues are counteracted by the psychotropic and addictive effect of THCJD.
6. Is THCJD legal in France?
Surprisingly, yes. THCJD is legal in France, as it is not on the list of substances prohibited by the French National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (ANSM) or the Ministry of Health.
But this relative legality must be qualified by two points:
- If tested, users who have consumed THCJD will definitely have THC in their blood and that is illegal;
- THCJD will most likely be banned in France in the near future. It will likely follow the same fate as HHC and its derivatives, which were banned in France in June 2023.






